High Court Says CDC Lacks Authority For Nationwide Eviction Moratorium
|
|
|
|
|
|
Displaying blog entries 421-430 of 1910
|
|
|
|
|
|

In today’s real estate market, low inventory and high demand are driving up home prices. As many as 54% of homes are getting offers over the listing price, based on the latest Realtors Confidence Index from the National Association of Realtors (NAR). Shawn Telford, Chief Appraiser at CoreLogic, elaborates:
“The frequency of buyers being willing to pay more than the market data supports is increasing.”
While this is great news for today’s sellers, it can be tricky to navigate if the price of your contract doesn’t match up with the appraisal for the house. It’s called an appraisal gap, and it’s happening more in today’s market than the norm.
According to recent data from CoreLogic, 19% of homes had their appraised value come in below the contract price in April of this year. That’s more than double the percentage in each of the two previous Aprils.
The chart below uses the latest insights from NAR’s Realtors Confidence Index to showcase how often an issue with an appraisal slowed or stalled the momentum of a house sale in May of this year compared to May of last year.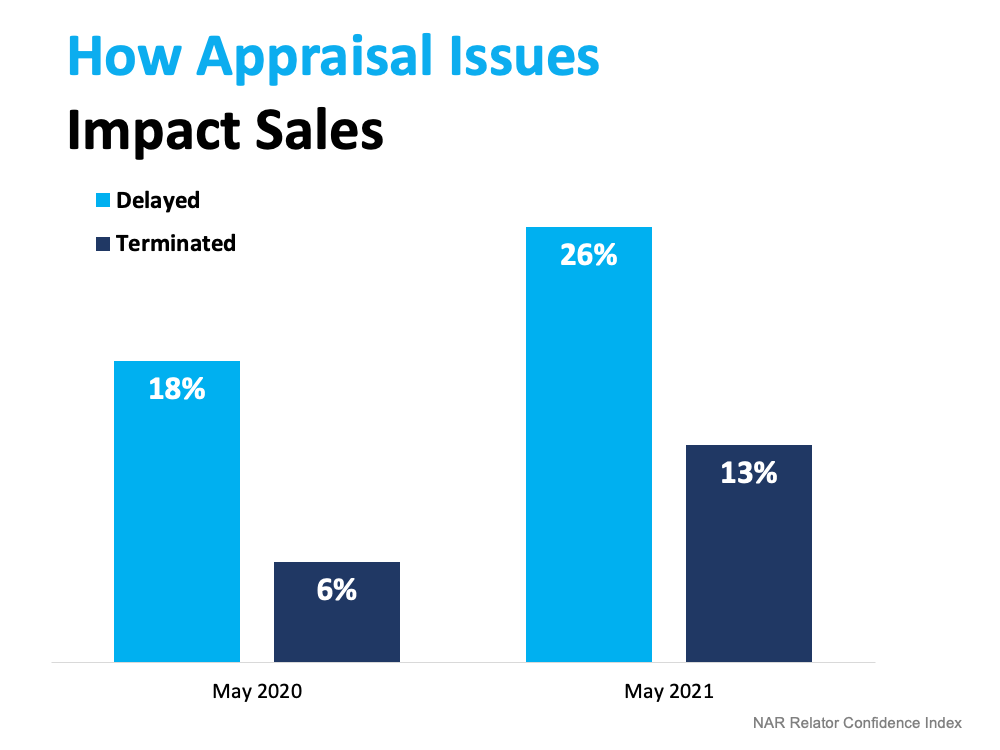 If an appraisal comes in below the contract price, the buyer’s lender won’t loan them more than the house’s appraised value. That means there’s going to be a gap between the amount of loan the buyer can secure and the contract price on the house.
If an appraisal comes in below the contract price, the buyer’s lender won’t loan them more than the house’s appraised value. That means there’s going to be a gap between the amount of loan the buyer can secure and the contract price on the house.
In this situation, both the buyer and seller have a vested interest in making sure the sale moves forward with little to no delay. The seller will want to make sure the deal closes, and the buyer won’t want to risk losing the home. That’s why it’s common for sellers to ask the buyer to make up the difference themselves in today’s competitive market.
Whether you’re buying or selling, let’s connect so you have an ally throughout the process to help you navigate the unexpected, including appraisal gaps.
![Homebuyers: Hang in There [INFOGRAPHIC] | MyKCM](https://files.mykcm.com/2021/06/24105823/20210625-MEM-1046x2093.png)
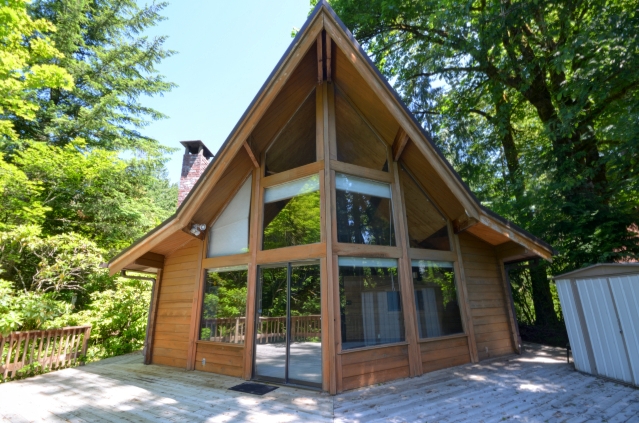
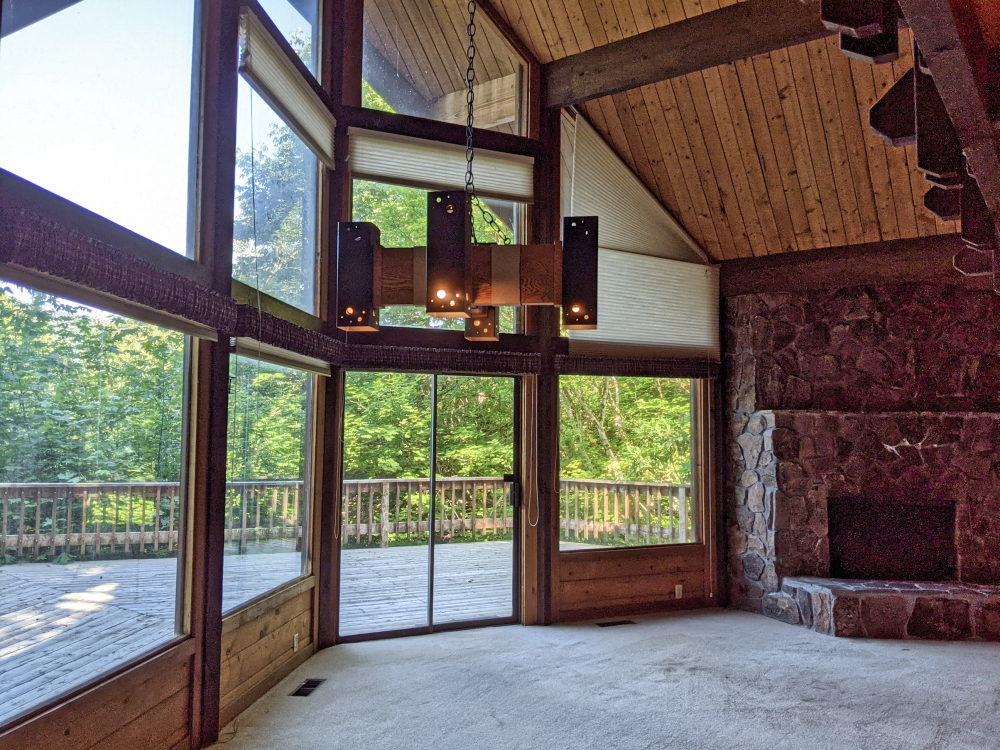
Here is the perfect Mt. Hood getaway located in the Timberline Rim subdivision above the Sandy River. Tons of wood throughout the home with high vaulted ceiling in the living room and tons of sun filled windows with natural light. Toe warming fireplace is ready to go after a day on the slopes. Two spacious bedrooms on the main level and a huge loft upstairs. $385000!



The pandemic created a tremendous interest in vacation homes across the country. Throughout the last year, many people purchased second homes as a safe getaway from the challenges of the health crisis. With many professionals working from home and many students taking classes remotely, it made sense to see a migration away from cities and into counties with more vacation destinations.
The 2021 Vacation Home Counties Report from the National Association of Realtors (NAR) shows that this increase in vacation home sales continues in 2021. The report examines sales in counties where “vacant seasonal, occasional, or recreational use housing account for at least 20% of the housing stock” and compares that data to the overall residential market.
Their findings show:
This coincides with data released by Zelman & Associates on the increase in sales of second homes throughout the country last year.
As the data above shows, there is still high demand for second getaway homes in 2021 even as the pandemic winds down. While we may see a rise in second-home sellers as life returns to normal, ongoing low supply and high demand will continue to provide those sellers with a good return on their investment.
If you’re one of the many people who purchased a vacation home during the pandemic, you’re likely wondering what this means for you. If you’re considering selling that home as life returns to normal, you have options. There are still plenty of buyers in the market. If, on the other hand, you want to keep your second home, enjoy it! Current market conditions show that it’s a good ongoing investment.
![Owning a Home Has Distinct Financial Benefits Over Renting [INFOGRAPHIC] | MyKCM](https://files.mykcm.com/2021/06/16121610/20210518-MEM-1046x2442.png)

The real estate market is soaring today. Residential home values are rising, and that’s a big win for homeowners. In 2020, there was a double-digit increase in home values – a trend that’s expected to head toward similar levels this year.
However, skyrocketing prices are causing some to start questioning affordability in the current housing market. Many are quick to emphasize the fact that homes today are less affordable than they were last year. Black Knight, a leading provider of data and analytics across the homeownership life cycle, just reported on the issue.
The findings show the historical averages of the national payment to income ratio, which they define as “the share of the median income needed to make the monthly payments on the median-priced home.” Their study reveals:
Right now, housing payments are slightly less affordable than the five-year average – but only by less than ½ a percentage point. However, they’re significantly more affordable than the 25-year average. Put another way, a buyer will likely make a slightly greater financial sacrifice to afford a home right now than if they purchased a home within the last five years. On the other hand, it also means the potential financial sacrifice is not nearly as great as it was over the last 25 years.
Last week, the Federal Reserve announced that, in the first three months of the year, household net worth increased by $968 billion based solely on the values of the real estate they owned. Another report from CoreLogic reveals the average annual gain in homeowner equity was $33,400 per borrower.
Homeownership continues to be the cornerstone to building personal wealth. For most Americans, their home is the largest asset they own. On top of that, the difference between the net worth of homeowners and renters is significant at every income level. Here’s a table detailing that point using data from a study done by First American: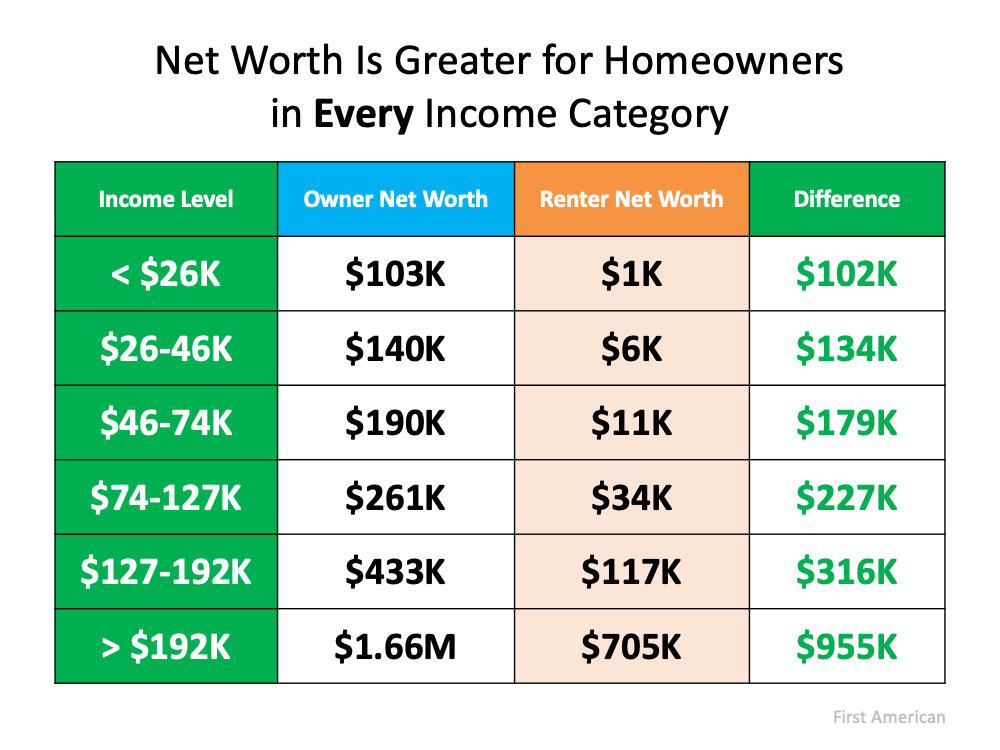 Owning a home is an essential steppingstone to grow a household’s net worth. Despite the slightly greater sacrifice in the percentage of monthly income you’ll spend on housing today, for most homebuyers, the payoff of starting to build equity now will be worth it.
Owning a home is an essential steppingstone to grow a household’s net worth. Despite the slightly greater sacrifice in the percentage of monthly income you’ll spend on housing today, for most homebuyers, the payoff of starting to build equity now will be worth it.
Since prices have risen dramatically over the past 18 months, it’s slightly less affordable to buy a home today than it was a year ago. However, when you consider the equity gain and weigh the long-term benefits of building your net worth, you may question if you can afford not to buy now.
Displaying blog entries 421-430 of 1910

