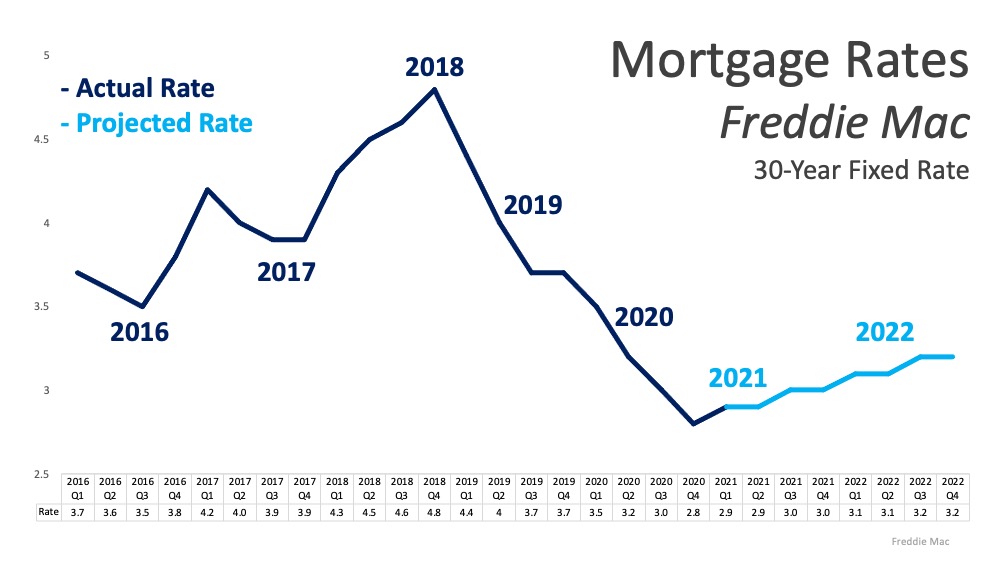
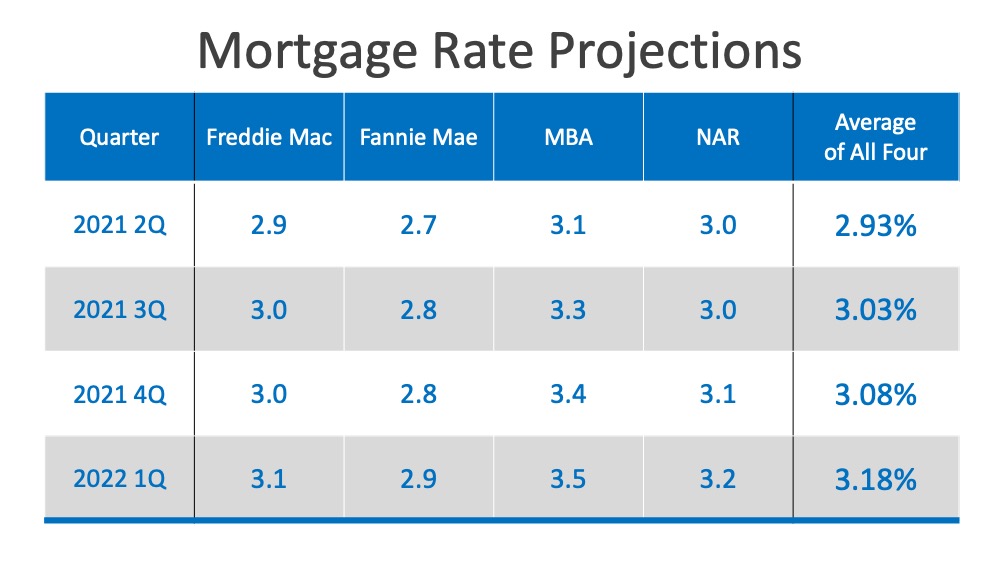
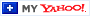
Home values appreciated by about ten percent in 2020, and they’re forecast to appreciate by about five percent this year. This has some voicing concern that we may be in another housing bubble like the one we experienced a little over a decade ago. Here are three reasons why this market is totally different.
1. This time, housing supply is extremely limited
The price of any market item is determined by supply and demand. If supply is high and demand is low, prices normally decrease. If supply is low and demand is high, prices naturally increase.
In real estate, supply and demand are measured in “months’ supply of inventory,” which is based on the number of current homes for sale compared to the number of buyers in the market. The normal months’ supply of inventory for the market is about 6 months. Anything above that defines a buyers’ market, indicating prices will soften. Anything below that defines a sellers’ market in which prices normally appreciate.
Between 2006 and 2008, the months’ supply of inventory increased from just over 5 months to 11 months. The months’ supply was over 7 months in twenty-seven of those thirty-six months, yet home values continued to rise.
Months’ inventory has been under 5 months for the last 3 years, under 4 for thirteen of the last fourteen months, under 3 for the last six months, and currently stands at 1.9 months – a historic low.
Remember, if supply is low and demand is high, prices naturally increase.
2. This time, housing demand is real
During the housing boom in the mid-2000s, there was what Robert Schiller, a fellow at the Yale School of Management's International Center for Finance, called “irrational exuberance.” The definition of the term is, “unfounded market optimism that lacks a real foundation of fundamental valuation, but instead rests on psychological factors.” Without considering historic market trends, people got caught up in the frenzy and bought houses based on an unrealistic belief that housing values would continue to escalate.
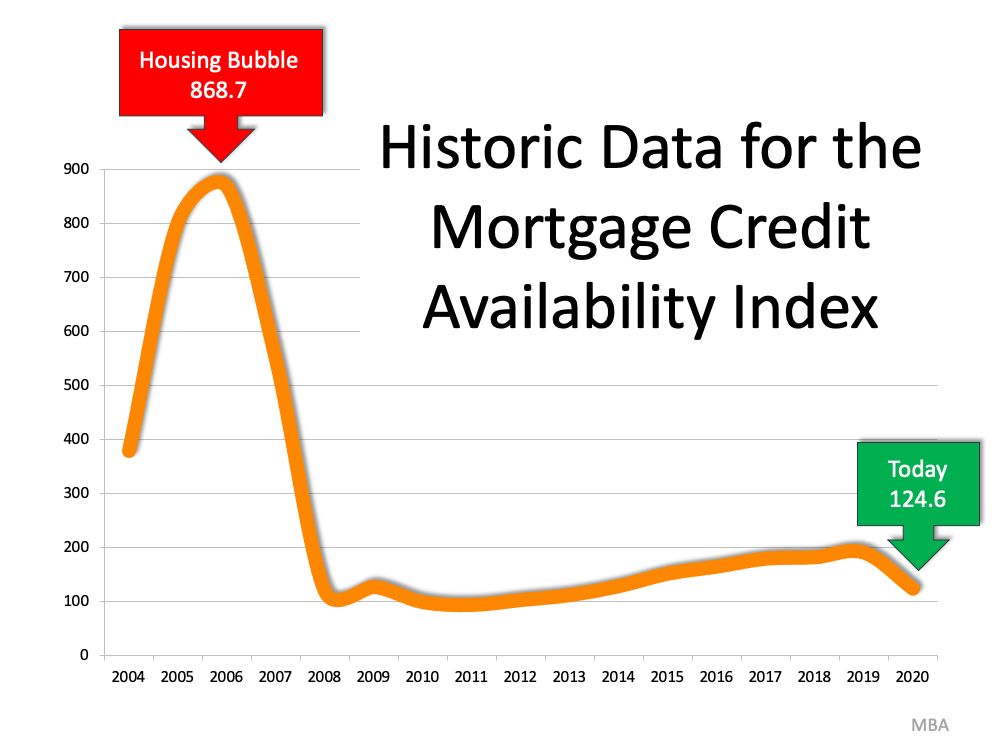
The mortgage industry fed into this craziness by making mortgage money available to just about anyone, as shown in the Mortgage Credit Availability Index (MCAI) published by the Mortgage Bankers Association. The higher the index, the easier it is to get a mortgage; the lower the index, the more difficult it is to obtain one. Prior to the housing boom, the index stood just below 400. In 2006, the index hit an all-time high of over 868. Again, just about anyone could get a mortgage. Today, the index stands at 122.5, which is well below even the pre-boom level.
In the current real estate market, demand is real, not fabricated. Millennials, the largest generation in the country, have come of age to marry and have children, which are two major drivers for homeownership. The health crisis is also challenging every household to redefine the meaning of “home” and to re-evaluate whether their current home meets that new definition. This desire to own, coupled with historically low mortgage rates, makes purchasing a home today a strong, sound financial decision. Therefore, today’s demand is very real.
Remember, if supply is low and demand is high, prices naturally increase.
3. This time, households have plenty of equity
Again, during the housing boom, it wasn’t just purchasers who got caught up in the frenzy. Existing homeowners started using their homes like ATM machines. There was a wave of cash-out refinances, which enabled homeowners to leverage the equity in their homes. From 2005 through 2007, Americans pulled out $824 billion dollars in equity. That left many homeowners with little or no equity in their homes at a critical time. As prices began to drop, some homeowners found themselves in a negative equity situation where the mortgage was higher than the value of their home. Many defaulted on their payments, which led to an avalanche of foreclosures.
Today, the banks and the American people have shown they learned a valuable lesson from the housing crisis a little over a decade ago. Cash-out refinance volume over the last three years was less than a third of what it was compared to the 3 years leading up to the crash.
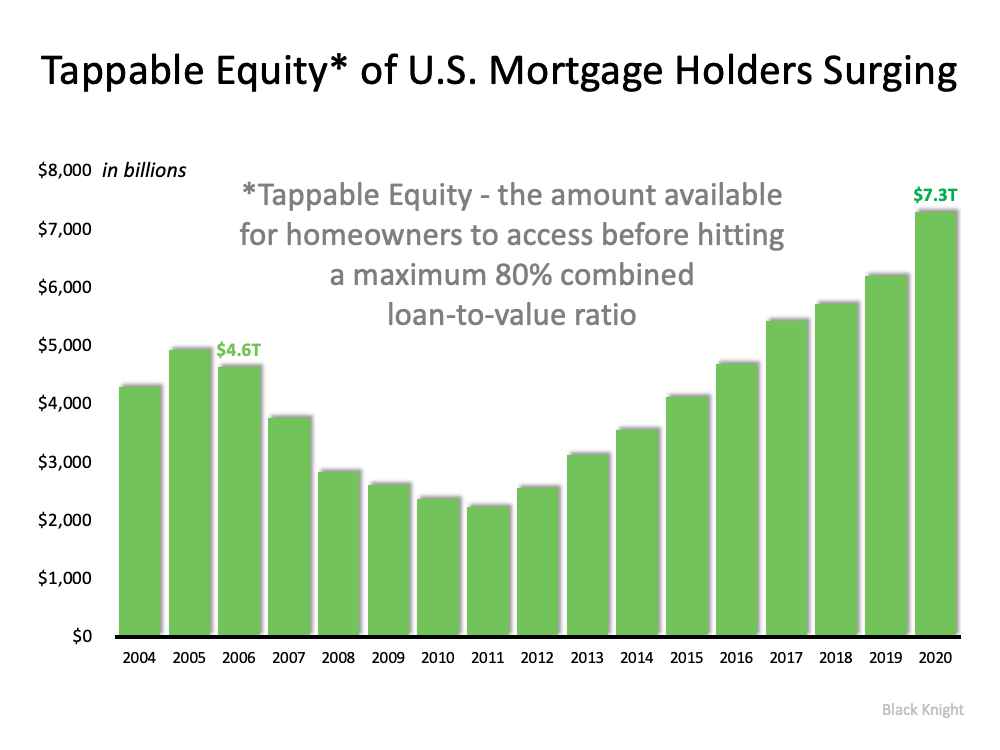
This conservative approach has created levels of equity never seen before. According to Census Bureau data, over 38% of owner-occupied housing units are owned ‘free and clear’ (without any mortgage). Also, ATTOM Data Solutions just released their fourth quarter 2020 U.S. Home Equity Report, which revealed:
“17.8 million residential properties in the United States were considered equity-rich, meaning that the combined estimated amount of loans secured by those properties was 50 percent or less of their estimated market value…The count of equity-rich properties in the fourth quarter of 2020 represented 30.2 percent, or about one in three, of the 59 million mortgaged homes in the United States.”
If we combine the 38% of homes that are owned free and clear with the 18.7% of all homes that have at least 50% equity (30.2% of the remaining 62% with a mortgage), we realize that 56.7% of all homes in this country have a minimum of 50% equity. That’s significantly better than the equity situation in 2008.
Bottom Line
This time, housing supply is at a historic low. Demand is real and rightly motivated. Even if there were to be a drop in prices, homeowners have enough equity to be able to weather a dip in home values. This is nothing like 2008. In fact, it’s the exact opposite.

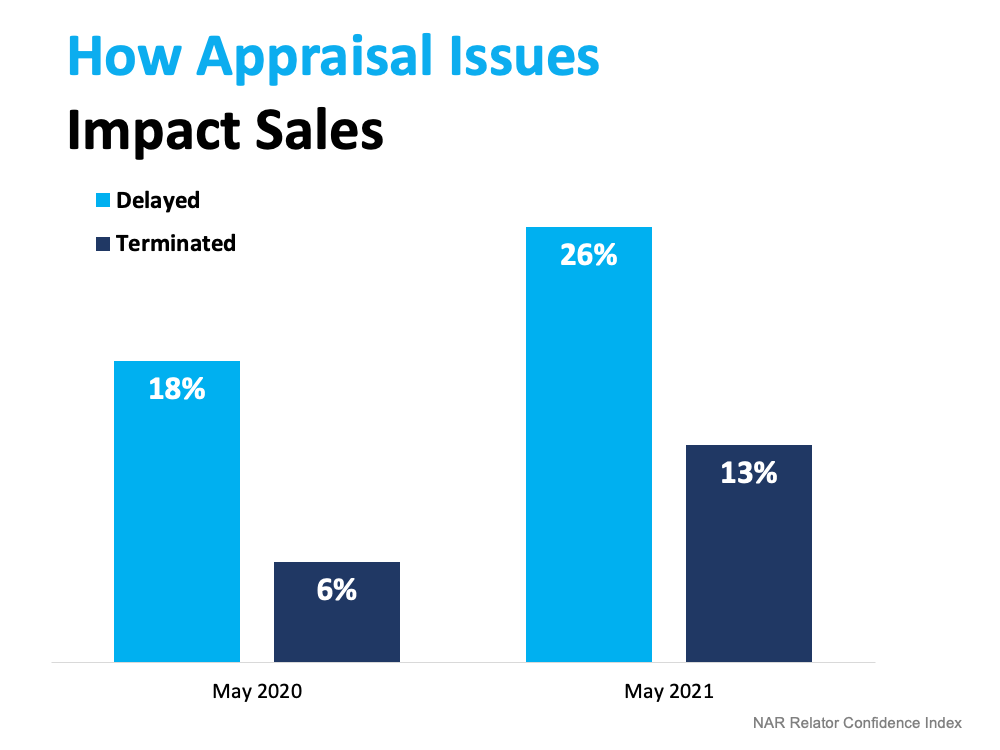 If an appraisal comes in below the contract price, the buyer’s lender won’t loan them more than the house’s appraised value. That means there’s going to be a gap between the amount of loan the buyer can secure and the contract price on the house.
If an appraisal comes in below the contract price, the buyer’s lender won’t loan them more than the house’s appraised value. That means there’s going to be a gap between the amount of loan the buyer can secure and the contract price on the house.
![Owning a Home Has Distinct Financial Benefits Over Renting [INFOGRAPHIC] | MyKCM](https://files.mykcm.com/2021/06/16121610/20210518-MEM-1046x2442.png)


.jpeg)